SBC 229: Basic
Biochemistry
Outline:
•Amino acids, the
fundamentals of protein structure, isolation and purification of proteins,
modification of proteins, and methods of determining protein conformation.
•Catalysis and enzyme
kinetics
•Ion transport and
other transport proteins
•Bioenergetics
•Glycolysis and the
citric acid cycle
•ATP synthesis and
membrane bound electron transfer in mitochondria
•Chloroplasts in
plants and algae
•Molecular motors, such as muscles, which
consume metabolic energy
AMINO
ACIDS
•organic molecules -
amine group, carboxylic acid group & a side-chain (R)
•4 key elements; C, N,
H & O
•R varies in size
•Have salt-like behavior – zwitterion
AMINO
ACIDS
•Classified by the
properties of side-chains
•all but glycine can exist in either of two
optical isomers, L or D; at least 1 chiral C
AMINO
ACIDS Nutritionally
•Essential:
Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Valine,
Histidine,
•Nonessential: Alanine, Aspartate, Glutamate*,
Tyrosine*Arginine*, Cysteine*, Glutamine*, Glycine*, Proline*, Serine*
Asparagine*
AMINO
ACIDS
•Aliphatic – hydrophobic;
core of a protein
•Acidic amino acids
- highly polar, negatively charged
•Basic amino acids -
positively charged
•Neutral polar
amino acids - not charged, R have polar groups which can form H bonds;
hydrophillic.
•Sulphur containing
amino acids - a sulphur atom, hydrophobic
•Aromatic amino
acids - an aromatic ring, highly hydrophobic
•Hydroxylic amino
acids - hydroxyl group
•Amidic amino acids - an amide group
The
primary structure
•-NH2 group at the left-hand end; -COOH group at
the right-hand end.
The
secondary structure
•Held together by hydrogen bonds between one of
the lone pairs on an oxygen atom and the hydrogen attached to a nitrogen atom:
The
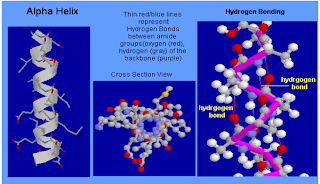
secondary structure- the alpha helix
•The pp chain is
coiled as a spring
•the carbonyl O of residue “i” forms a H bond
with the amide of residue “i+4”
The secondary structure- the alpha helix
The
secondary structure - Beta-pleated sheets
•Protein is arranged
in a sheet.
•Rs would be above and below the plan of the
sheet. H bonds between the CO and the NH groups
The
tertiary structure
•A description of the folding of a protein to
its final 3-dimensional shape
Quaternary
protein structure
•Regular association
of two or more pp chains to form a complex
•May be composed of two or more identical
polypeptides, or different polypeptides







No comments:
Post a Comment